The Root of Many Plant Problems in Central Ohio: Soil pH
By Walter Reins
ISA Certified Arborist
January 16, 2025
[Please note: This article was revised and republished on 1/16/25 from its original publish date of 4/24/24.]
You’ve probably heard the term pH. You may even think “I know this one - it means something is either acidic, neutral, or alkaline”, and that wouldn’t be wrong. But what does that mean and why does it matter? What determines the pH of soil, water, or even the human body? Like the periodic table of elements, pH may be something that reminds you of high school chemistry class, something you’ve filed away under the “when am I ever going to use this?” section of your brain, long ago forgotten and collecting dust ever since it was put there. While pH is far from being an endorphin-producing topic, it does significantly influence plant growth and overall health in your landscape. Let’s discuss the role that soil pH plays in nutrient availability, soil chemistry, and even microorganism activity, and why it matters for your plants.
pH and How It’s Influenced
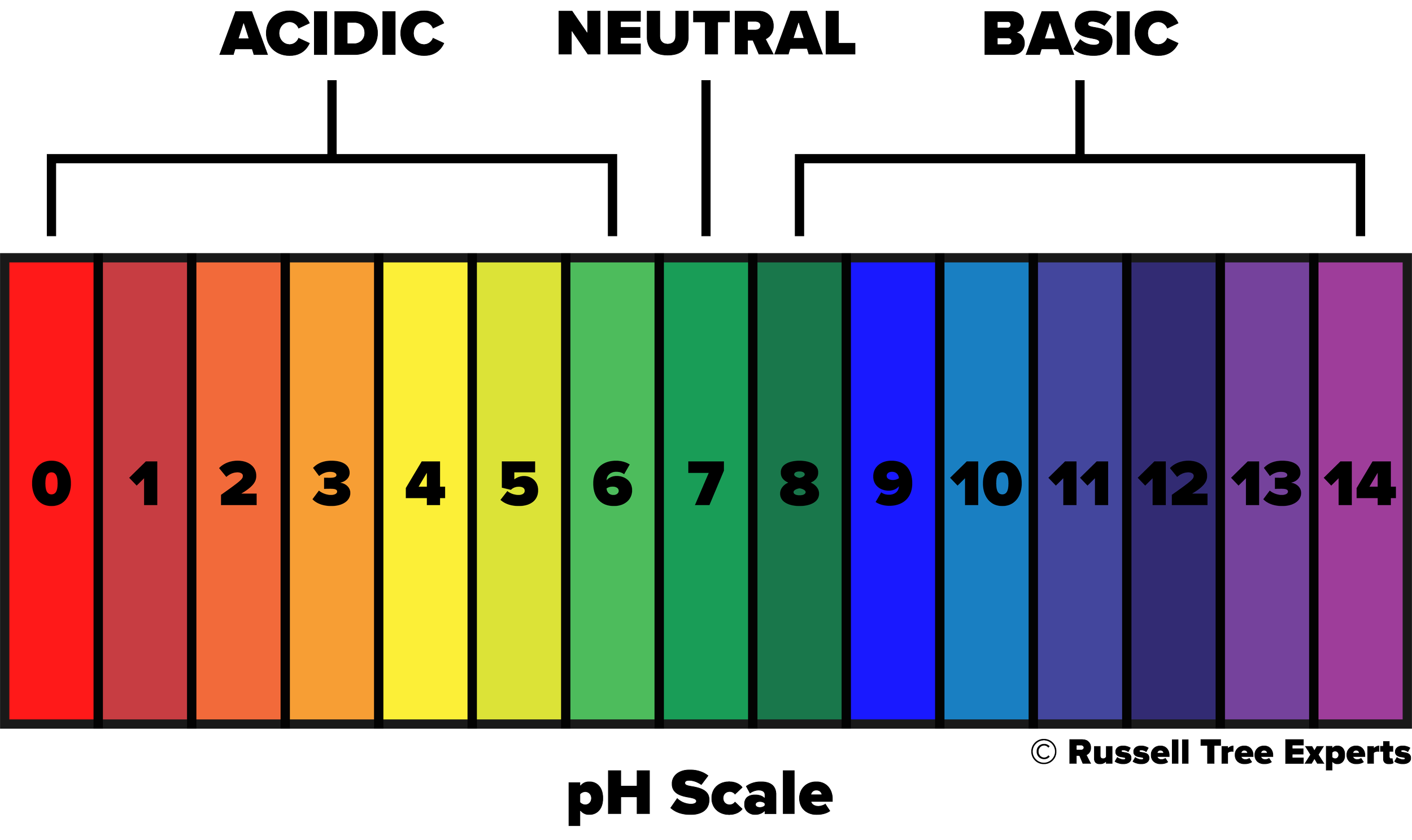
pH stands for “potential of hydrogen”, and is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14 with 7 being neutral. A value below 7 is considered acidic while a value above 7 is considered alkaline (or basic). This scale represents the concentration of hydrogen ions present, with acidic solutions having a greater number of ions and alkaline solutions having fewer ions. In soils, that concentration of hydrogen ions is influenced by things such as the parent rock material that originally formed the soil, human activity, climate, and the presence or lack of organic matter. In turn, the resulting pH will influence the availability of nutrients essential for plant growth, microbial activity that helps with nutrient absorption, and soil chemistry that influences the breakdown of soil particles into more usable forms. Of the influencing factors mentioned above, parent rock material and the presence or lack of organic matter often go hand in hand and are the most significant influencers in our central Ohio landscapes. Central Ohio largely consists of limestone bedrock, which naturally has a higher pH than what’s preferable for most plants. So you might ask “Well, how is it then that any plants can be healthy and thrive in central Ohio?”. The answer is organic matter. In an undisturbed, natural environment like the forest, years and years of organic matter have formed on top of the infamous “Ohio clay” subsoil that we encounter in our backyards. The source of this organic matter comes from falling leaves, dead branches and trees, and dying organisms just to name a few, that collect on the forest floor year after year, decade after decade. These are all things we tend to remove from our landscapes to keep them tidy, which results in a lack of organic matter formation over time. For more on how to address this topic, check out our Arbor Ed article “Leave those Leaves!”
Nutrient Availability
Chlorosis in a pin oak tree in Bexley, Ohio
pH influences the availability of essential nutrients in the soil by changing their level of solubility. This simply means that pH will determine whether or not these nutrients are in a form that can be absorbed by the tiny roots and roots hairs of plants. Most plants will prefer growing in soil with a pH range between 6-7, slightly acidic to neutral. When the pH is out of its optimal range for a particular plant (generally too high in central Ohio), the plant’s growth may slow, it may lose overall health and vigor, or conditions like chlorosis can develop because that plant isn’t getting the nutrients it needs to carry out essential functions for growth. Chlorosis, or yellowing of leaf tissue, is a very common condition in central Ohio and can be seen most often with trees like pin oak, red maple, white pine, and river birch. It’s interesting to note that these are trees that are either native to Ohio or an adjacent region. In their natural habitats where organic matter is abundant, soil pH is lower and nutrients are readily available for uptake. The parent material, derived from limestone and having higher pH levels, does not affect the trees since the absorbing roots are largely growing in the organic layer above it. In our backyards however, carpeted with lawn but cleared annually of leaves, higher pH levels can quickly cause issues even with otherwise healthy trees.
Chart showing availability of essential elements at various pH levels
Microbial Activity
pH affects the activity of microorganisms in the soil. These microorganisms are essential for plant health, helping plants to absorb certain nutrients, or aiding in the breakdown of organic matter into available forms for your plants. Certain fungi, bacteria, or insects that benefit a particular plant will naturally thrive in the same pH that is ideal for that plant. Encouraging the proper pH for your plants in turn helps to foster a healthier population of these important helpers in the soil. In the same way that our own bodies are influenced by the health of our gut bacteria, plants rely on microbial activity in the soil. Without it, they can struggle to carry out essential functions for proper growth and overall health.
Soil Chemistry
Similar to nutrient availability, pH can affect the chemistry of the soil and determine whether or not the available nutrients will be absorbed by roots. It also influences the composition of the soil, helping certain minerals to break down into smaller molecules, ultimately affecting the charge of soil particles and the ability for the soil to hold on to essential elements that could otherwise be removed from the soil. A good example of this would be a soil’s ability to retain certain nutrients by preventing them from getting washed out of the soil by irrigation or rainfall. Acidic soils tend to be better at retaining more of these charged nutrients. It's no coincidence then that most plants prefer acidic or slightly acidic soils, as the lower pH makes those soils richer in nutrients and more “user friendly” for plants.
~
Soil pH plays a significant role in the overall health of trees, shrubs, and other plants in our landscape. A little bit of knowledge can go a long way in helping to understand the unique issues you may have in your central Ohio landscape. Below is a list of a few things you can consider in determining what’s best for your yard.
Have a soil sample from your yard submitted for analysis to help determine if there is a pH issue or nutrient deficiency.
If you know that you have higher pH levels, consider planting trees and shrubs that are more tolerant of alkaline soils.
Try incorporating more organic matter into your soil by allowing leaves to decompose in landscape beds over the winter, and consider enlarging groundcover or mulch beds around trees (less lawn)
Have root zone invigoration work done for trees that are struggling with nutrient deficiencies and/or soil compaction.
Apply pH lowering products to landscape beds with particularly sensitive trees or shrubs (note that this is something that generally needs done annually, as permanently lowering the pH of soil with additives is next to impossible).
As always, one of our 20+ ISA Certified Arborists® are happy to provide a free tree quote by giving us a call at (614) 895-7000 or by visiting RussellTreeExperts.com/Quote
Additional Tree Preservation Articles!
Walter Reins I Regional Manager, Russell Tree Experts
Walter became an ISA certified arborist in 2003 and has a degree in landscape horticulture. He has 25 years of experience in the tree and landscape industries and originally began working at Russell Tree Experts in 2011. Walter is also the owner/operator of Iwakura Japanese Gardens, a small design/build/maintenance firm specializing in Japanese-style gardens, and also offers responsible tree planting for all landscapes.